Until recently, only industry titans like Microsoft, Amazon, and Google could successfully and effectively harness continuous, real-time data—much less use these statistics to fuel events-based billing models. Backed by an army of developers, data engineers, and finance professionals, events-based billing allowed these large companies to directly link the value their services provided with the cost presented on a customer’s invoice.
However, with the introduction of Maxio’s Events-Based Billing, this next generation billing model is now available to every business—no development required. Large IT budgets, legions of developers, and seemingly endless financial resources are no longer a requirement. Even small and medium-sized businesses can offer pricing models like the industry titans.
You may be asking: why should your organization adopt an events-based billing model? And how do you do it? We’ll help you answer these questions by looking at how two industry leaders, AWS and Twillio, have found success from their own events-based billing models.
What Amazon Web Services and Twilio Get Right
As of late 2019, Amazon Web Services (AWS), accounts for about 71% of its parent company’s operating income and about 13% of the brand’s overall revenue. Put another way, cloud services are a huge part of Amazon’s 1,233% stock surge over the last decade.
Despite being a much younger company, Twilio, the cloud-based communications tools and services company, has established a business and billing model that is made to last. In just the last year, Twilio saw revenue jump 57% year over year as customer accounts rose 23%.
Though they offer two very different services, AWS and Twilio have both harnessed the power of their events-based data to provide their customers with flexible, value-based pricing. Twilio’s pricing structures include offering customers monthly recurring charges or pay-as-you-go options based on user events. This events-based billing model was, of course, pioneered by Amazon in 2006 and has since been the catalyst for Amazon’s rapid growth and dominance in the marketplace.
How AWS Uses Events-Based Billing
When AWS first entered the cloud services business over a decade ago, the SaaS market was known for subscription-based business. Customers entered into annual (or, in some cases, multi-year) contracts that locked them into certain prices and usage levels. So, when Amazon launched a new cloud services business model which involved no upfront agreement beyond price-per-event, they immediately caught other services providers off guard. AWS’s new events-based model offered customers the ability to pay as they went without locking themselves into daunting long-term contracts. This translated to customers only paying for what they consumed and nothing more, lowering the risk of entry for new business and empowering Amazon to quickly gobble up market share.
As if that wasn’t enough to buck the trends, AWS couples their event-driven pricing model with volume discounts. Amazon customers pay less as they use more AWS services, and they have the opportunity to select a billing model that allows them to “save” or retain unused capacity from one period for future use in another billing period. Combined, these billing models have made AWS an attractive service provider for businesses of every size and across the maturity spectrum because, unlike structured contracts, this flexible billing model helps organizations stay agile. They can scale up their capacity or service usage to meet their own customers’ demand or scale down to save costs during slower periods.
How Twilio Uses Events-Based Billing
Twilio is a provider of cloud-based communications tools that serve as the backbone of Lyft, Yelp, Airbnb, and Shopify, a space in which many market analysts see huge potential for growth.
No matter the industry—whether the customer is the ride-sharing giant Lyft or a recent startup—all Twilio customers have the opportunity to pick from two pricing models: monthly recurring charges or pay-as-you-go. In both cases, Twilio’s billing model allows for scalability for both the company and its customers.
Under their monthly payment model, customers pay a flat rate based on the services they select for that month, regardless of the amount consumed. This is a classic subscription. To get customers started with this model, Twilio packages their typical services based on recent customer demand and new related features.
Twilio’s pay-as-you-go model is just like AWS’s, but with a slight twist: instead of billing in arrears based on consumption, Twilio bills their customers upfront with a model similar to a retainer: customers’ usage is deducted from their balance held by Twilio. Once a customer reaches zero, they can no longer use Twilio services (at least, until they refill their balance). However, if they have money left in their retainer, those funds can carry over to future usage.
Creating Your Own Events-Based Billing Model
In the case of Twilio, AWS, and many other SaaS giants on the market, the common threads across their events-based billing models are flexibility and precision. Flexibility means customers have the ability to choose their payment structure from available options while also allowing for variability from month to month. In regard to precision, these SaaS providers are able to present invoices to customers with detailed usage statistics that enables customers to directly link the price they pay to the value received.

Are you still operating in the data dark ages? Sign up for our free Real-Time Data course to learn how your business can (and should) leverage real-time data streaming.Business Email*
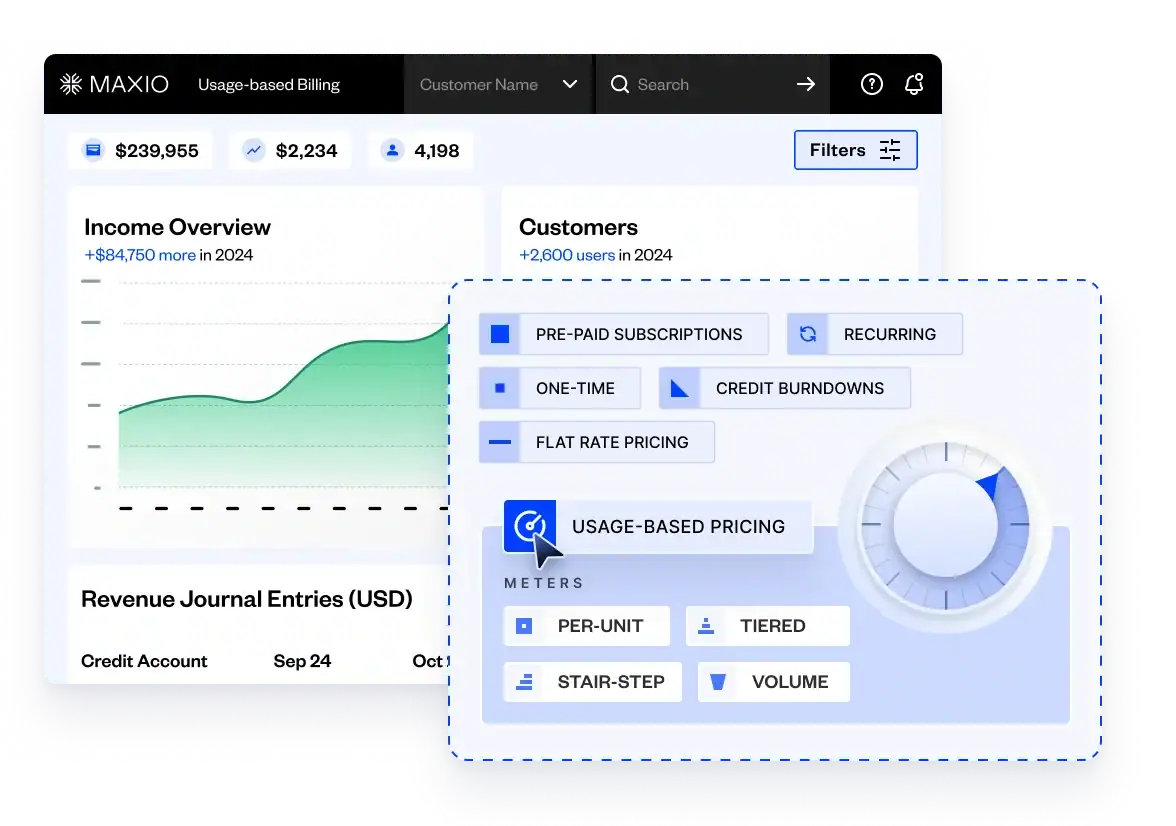
With the new billing management systems available through Maxio, this next generation billing model is now accessible to everyone who wants to leverage events-based pricing for growth—no matter how large or small their business is.
Setting Up Events-Based Billing with Maxio
Setting up events-based or pay-as-you-go billing is a bit more complex than just assigning a fixed price to a product and invoicing against it at the end of a billing period.
There are generally five high-level steps involved to implement an Events-Based Billing model.
1. Find Your Billable Metrics
The first step includes determining the billable metrics your company will use to measure the value your customers receive from your service. These metrics should be specific to your organization’s product offering. Some common metrics include:
- Communication Events: The number of sends or receipts from messages, calls or any other communication method. Examples include message or call minutes, as in the case of Twilio, or messages delivered successfully or call duration in other cases.
- Data Events: The amount of data stored, used, or processed via your platform. An example of this is API calls and vCPU service hours like Amazon (AWS). You can also leverage clicks (Google Ads), data requests, form entries, or page views.
- Usage Events: Any measurable way of your customers using your products and services, such as transactions processed, queries, security activity and log sizes.
2. Choose Your Pricing Model
Once you have selected your company’s billable metrics, it is time to select the events-based pricing model to offer your customers.
As we saw in our two examples above (AWS and Twillio), there’s more than one way to implement events-based billing. You could charge based on the summation of everything submitted or limit it to a summation of only unique values submitted. You can take averages or look at min/max quantities and even percentages or standard deviations. You can slice and dice your event data almost any way you want.
From there, you can add further specification to your per-unit prices. (Will they change when your customers consume more or less of your platform, like Amazon’s do?)
Finally, you can decide if you would like to price on a single attribute such as “messages delivered,” or vary your price based on multiple attributes, such as “messages delivered by country.” Regardless of how simple or complex you wish to make your events-based billing model, the right configuration is available to you.
3. Capture and Monitor Customer Events Data
Once your billable metrics are assigned and your customers begin to utilize your services, your platform will need to feed that fully-attributed event data into Maxio. Maxio integrates directly with your enterprise infrastructure via API to structure, route, and record customer usage levels.
This integration can seem complex because customers utilize services across different platforms and data can flow in from different systems in different formats, time frames, and loads. However, because of Maxio’s single API endpoint, this data collection is simplified regardless of where the data is coming from.
4. Apply the Pricing Plan
In this phase, Maxio will apply your customer’s pricing model against the consolidated events-based data collected specifically for them. Since you are now varying your billing based on different attributes, communication is especially important. Help your customers understand their bills with transparent invoices.
5. Bill Customers
Events-based billing invoices are created at the end of the designated billing period, displaying the details that allow customers to easily link their charge with the services received.
Your billing management system should also be configured to offer customers more than one payment option. Allowing for flexibility in payment methods helps control some of the factors that influence involuntary churn, where invalid or expired payment information prevents payment or service renewal. Through Maxio’s dunning functionality you can also decrease involuntary churn by setting up dunning flows and messaging specific to your events-based products. This targeted messaging goes a long way to help your events-based customers continually renew.
Leverage Your Events Data to Create Events-Based Billing
No matter how you leverage events-based billing, providing flexibility and detail around your pay-as-you-go model drives customer satisfaction and loyalty. Events-Based Billing can also enable you to target customer markets that were previously out of reach.
If you’re ready to establish events-based billing for your company with the same level of precision as the big players in the market, Maxio’s team is ready to help you learn more.